In general, the main difference between Processor vs Motherboard is that the motherboard allows communication between computer components such as the processor, memory and peripheral connectors, while the processor delivers instructions of a computer program to perform arithmetic, logical and control operations specified in the program.
CPUs, memory, and peripherals can communicate with a motherboard, instead of a processor. A processor is a component of a computer that carries out instructions for computing. check also b550 vs x570
Computers are capable of performing multiple tasks simultaneously. Many components make up a computer. Software and hardware components are divided into two categories. Neither the motherboard nor the processor are software components. It is the motherboard that communicates with other units, while the processor performs other tasks. A computer will function properly only if both components are present.
What is a Motherboard?
Printed circuit boards act as the main interface between a computer and other peripheral devices. These components communicate with each other as well as with other system components, such as the central processing unit and memory, and provide connectors for other devices.
Table of Contents
Types of Motherboards: Complete Guide
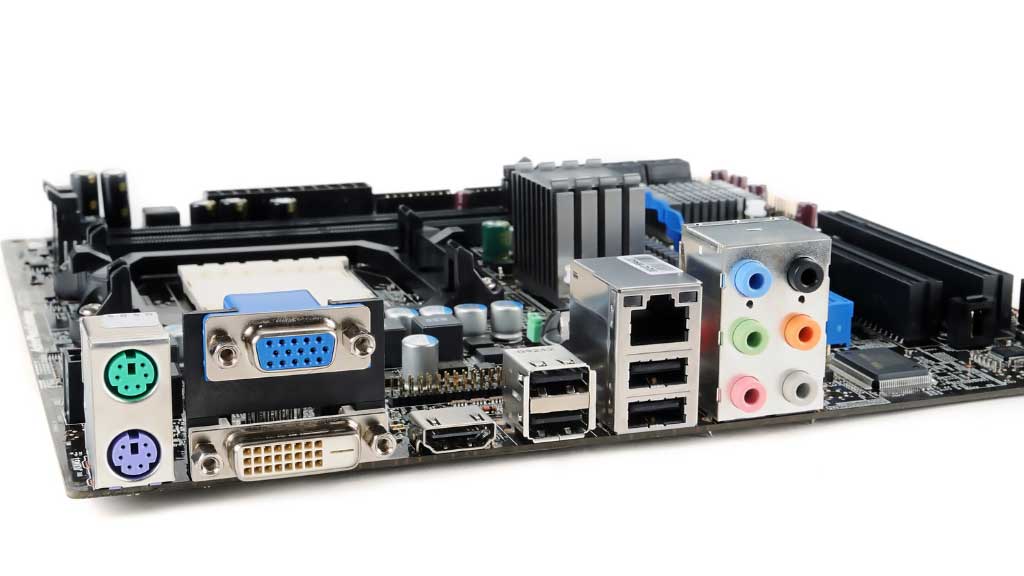 Here, we have a list of the different types of motherboards along with a description of their looks and features.
Here, we have a list of the different types of motherboards along with a description of their looks and features.
-
AT Motherboard:
This is an ancient type of Motherboard. AT refers to the Advanced Technology (AT) power connector, whether they have them or not. From the mid-1980s to the mid-1990s, AT motherboards were between 13.8 and 12 inches. On this motherboard, new drives cannot be installed. Below is an image of an AT Motherboard, which was used in the 286/236 and 436 computers.
-
ATX Motherboard:
At the time of its development, this Motherboard configuration was called Advanced Technology eXtended and is still used today. Compared to the previously working Motherboard, such as AT, the ATX has improved greatly.
There are many variations of ATX Motherboards (including microATX, FlexATX, nano-ITX, and Mini-ITX). ATX boards range in size from 12 by 9.6 inches to 16 by 19 inches. Also, the ATX Motherboards have been upgraded quite a bit in recent years.
-
Modern ATX Motherboard
Modern ATX Motherboards have many advantages over their predecessors. These are some of the features and uses of modern ATX Motherboards
- Power phases for cleaner and more stable power.
- This will allow for the bigger heatsinks found on aftermarket CPUs.
- Improved graphics card cooling by making expansion slots wider.
Overclocking is superior when all factors are taken into account. It is also worth noting the spacious ATX full-tower and mid-tower cases that can fit a half dozen fans, water cooling setups, tall heat sinks (for the CPU and RAM), and so much more.
-
Micro-ATX Motherboard
In terms of size, it’s smaller than ATX Motherboards with a 9.6 x 9.6 inch footprint. A dimension of 9.6 x 8.1 inches is offered by some manufacturers. At least seven PCI or PCI-Express expansion slots are available on modern ATX motherboards, while only four slots are available on microATX boards.
- There are fewer ports and slots on this board than the ATX Motherboard.
- Compare budget motherboards to other ATX and ITX boards.
-
Mini ITX Motherboard
Mini ITX motherboards measure 6.7 x 6.7 inches, which is smaller than any conventional Motherboard. Here are some of the advantages and features of mini ITX motherboards.
- A fan-less cooling system and small size enable it to consume less power.
- As an alternative to ATX, Micro-ATX, or another ATX variant, Mini ITX boards can also be used.
-
E-ATX Motherboard
The E-ATX Motherboards are larger than ATX Motherboards, and they are extended ATX Motherboards. Even though it is a small board, it has a lot of features that other typical motherboards do not have. Gaming is the primary purpose of the E-ATX. It can accommodate a powerful CPU with many cores and huge amounts of memory. Below are a few advantages and features of the E-ATX Motherboard.
- In addition to PCI slots, it has DIMM slots as well.
- Besides WiFi, sound cards, and onboard troubleshooting features, these boards have powerful VRMs.
- A maximum of 128GB of RAM is available on this motherboard.
The type of Motherboard used for conventional computers. It also comes with features like overclocking, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, thunderbolt expansion, and liquid cooling. Therefore, these motherboards are the best for building PCs that have mind-blowing components.
Motherboard Components
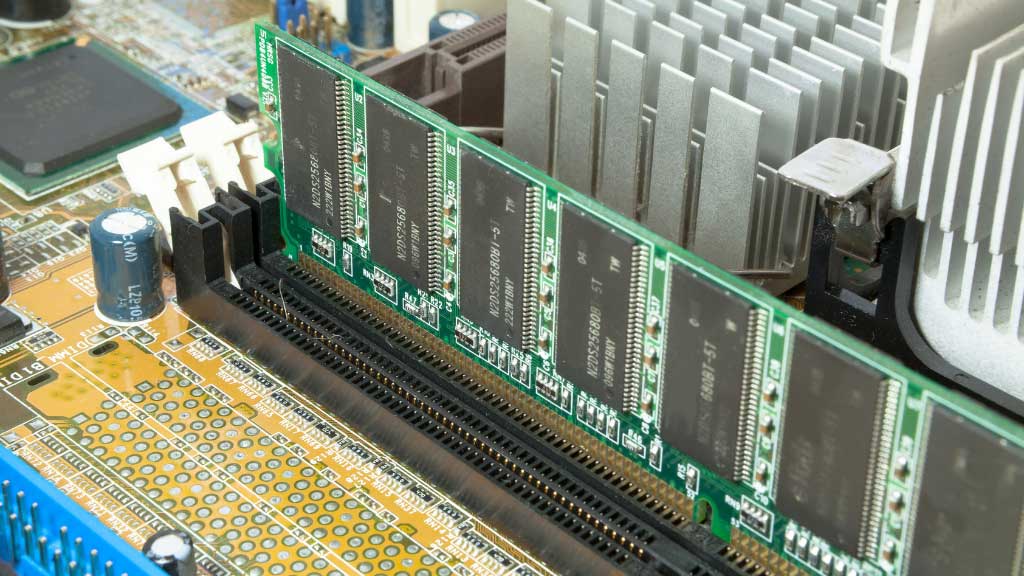 Motherboards are composed of various components that each play a specific role in the functioning of a computer. A typical Motherboard is described in detail below. We will describe each component below.
Motherboards are composed of various components that each play a specific role in the functioning of a computer. A typical Motherboard is described in detail below. We will describe each component below.
Expansion Slots
In expansion slots, such as a WiFi card, a network card, and a sound card, extra memory may be inserted.
-
ISA Slots
There have been only a few expansion slots on Motherboards since the early days. The black color of the AT boards identifies them. These slots were used to install displays or sound cards. Industrial Standard Architecture is the full name of this 16-bit bus.
-
PCI Slots
PCI stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect. In today’s world, PCI slots on Motherboards are one of the most important components and are widely used for adding more cards to the board. Unlike the PCI bus, the PCI high-speed bus supports 64-bit data.
PCI Express
They are Motherboard’s newest and fastest component for adding on cards, also known as PCIe. The serial bus supports full-duplex operation.
-
AGP Slot
An AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) is a specific interface for installation of graphics cards. AGP is also a popular option for gaming display cards, along with PCIe.
RAM(memory) Slots
-
SIMM Slots
Single inline memory modules are the full form. Motherboards with these slots were found as far back as the 486. The SIMM supports a 32-bit bus.
-
DIMM Slots:
Dual inline memory module is the full form of DIMM. They run on a faster 64-bit bus that runs on the latest RAM slots. SO-DIMMs are the DIMMs used on laptop boards.
CPU Sockets
In order for a CPU to be installed on a Motherboard, the CPU socket is essential. These sockets are explained below.
-
BIOS
This system is commonly referred to as the Basic Input Output System, or BIOS. The Motherboard component is an integrated chip. The BIOS chip stores all the information and settings of your Motherboard, which can be modified via the BIOS mode in your computer.
-
CMOS Battery
Lithium-ion button cell, 3.0 Volts. COMPLETE METAL OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR is the cell responsible for storing BIOS data. A CMOS battery is usually called CR-2032.
-
Power Connectors
Motherboards are connected to SMPS via connectors.
An AT connector consists of two sets of six male pins and is used on old types of motherboards.
They are either 20 pin or 24 pin female connectors. The ATX connectors are the latest in the power connector series. Featured on all the latest types of Motherboards.
-
IDE connector
A disk drive is interfaced using the Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) connector. Floppy Disk Drives are connected with the 34-pin male connector and IDE hard disk drives with the 40-pin male connector.
-
SATA connector
Solid-state drives, optical drives, and hard disk drives are all connected to host bus adapters via a SATA interface. IDE connections are much slower than serial advanced technology attachments (SATA) interfaces.
What is a processor (CPU)?
 Central processing units are electronic circuits that allow computer programs to run. It follows a program’s instructions to perform basic arithmetic, logic, control, and input/output operations.
Central processing units are electronic circuits that allow computer programs to run. It follows a program’s instructions to perform basic arithmetic, logic, control, and input/output operations.
Types of Processors
An embedded system can have a variety of processor types. There are five types of general-purpose processors, Microcontroller, Microprocessor, Embedded Processor, DSP, and Media Processors.
-
Microprocessor
General-purpose processors are represented by microprocessors in embedded systems. Different types of microprocessors are available on the market from various companies. The microprocessor is also known as a scratchpad register, control register, or status register, and it has an ALU, or application logic unit.
Various kinds of memory and external connections, such as interrupt lines, lines for memory access and ports for communication, may be present on a chip. Inputs and outputs can both be programmed using these ports, so we can use them either way. The following are general-purpose processors that can be used with Linux.
-
Microcontroller
Microcontrollers are basically computers that come in different packages and sizes. During the basic operation of the microcontroller, input and output are read and responded to. General Purpose Input Output (GPIO) describes it. Some of the microcontrollers are Microchip Atmega328-AU, Microchip P1C16F877A-I/P, Microchip P1C16F1503-I/P, Microchip P1C16F671-I/SN, Microchip P1C18F45K22-I/P, etc.
-
Embedded Processor
Embedded processors control electronic and mechanical functions simultaneously. A processor, a timer, and an interrupt controller are part of the system. The program memory and the data memory, the power supply, the reset and clock oscillator circuits, the application-specific circuits, and the ports and interfaces.
-
Digital Signal Processor
Analog and digital signals may be measured, filtered, and compressed using digital signal processors. Analyzing and manipulating signals is signal processing. Clear signals may be obtained by means of computers, Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs), or Digital Signal Processors (DSPs). Mobile phones, printers, oscilloscopes, barcode scanners, and other devices use DSP processors. Fast and dependable, these processors run real-time applications
-
Media Processor
An image/video processor is a real-time media processor. In addition to voice user interfaces, audio processors are used in professional audio applications. There are additional media processors besides TN2302AP IP, IN2602AP IP, DM3730, DM3725, M37385, M388, TMS320DM6467, and TMS320DM6431.
-
ASIC Processors
Specific ASICs are built for specific applications. Chips with this size and power consumption are very attractive. This is the main drawback of ASICs. Chips like these are used in satellites, modems, computers, etc. ASIC manufacturer Bitfury is among the best in the business. Companies: XMOS Semiconductor Private Company, Analogix Semiconductor Private Company, EDAptive Computing Private Company, Lumen Radio Private Company, Integrated Device Technology, Hookit. Companies, etc
-
MultiProcessor
A multiprocessor is a computer with multiple CPUs. A tightly coupled system is one in which one CPU shares memory, a bus, and peripherals. Multiprocessors feature increased performance, reliability, and scalability. Processors like these are used when a large amount of data needs to be processed at a rapid pace.
Difference Between Processor vs Motherboard
 There are two basic parts of any computer: the motherboard and the CPU. The CPU and motherboard must both perform critical functions to run the operating system and programs of the computer. Motherboards provide connections among computer components, while CPUs do the actual computation and data processing. The hard drive of an office computer can be replaced, with some restrictions, but replacing the motherboard requires rebuilding the entire system.
There are two basic parts of any computer: the motherboard and the CPU. The CPU and motherboard must both perform critical functions to run the operating system and programs of the computer. Motherboards provide connections among computer components, while CPUs do the actual computation and data processing. The hard drive of an office computer can be replaced, with some restrictions, but replacing the motherboard requires rebuilding the entire system.
Processor Compatibility
The CPU socket on the motherboard must match the processor socket on the processor. A motherboard that is incompatible with a processor will not work. Every few years, developers create new CPU sockets, which limits CPU upgradeability. A computer that is out-of-date requires a motherboard replacement, which is as difficult as building one from scratch, or a new CPU.
Other Compatibility
In addition to hard drives and RAM, almost all computer components must be compatible with a motherboard. IDE hard drives, for example, cannot be installed on a motherboard with modern SATA ports. There are some RAM models that don’t work with specific CPUs — processors also have compatibility issues — but the vast majority of parts are compatible with the motherboard.
Processor Functions
Most of the computations and functions required to run an operating system on a computer are handled by the CPU. A processor may handle all the data for a system, while an add-in card, such as a graphics card, may offload some of it. When it comes to determining the speed of a computer, the processor is more important than the graphics card.
Motherboard Functions
Often referred to as the brain of the computer, the motherboard is home to a variety of slots and connectors. Connected to the motherboard, every component in a computer transmits data to and from each other. In addition to processing audio data, many motherboards include a chipset for handling sound, so you don’t need separate sound cards. On traditional computers, graphics processors were built into the motherboard, but nowadays computers use either separate graphics cards or graphics technology built into the processor.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is the difference between a processor and a motherboard?
The two computers perform their tasks at vastly different levels, so there is a huge difference between them. They differ in this way. PCs work better and communicate better when they have a solid motherboard to power them. The motherboard is organized for PC reasons.
Your motherboard connects every function of your computer so that it can work smoothly. As a result, the processor distributed proper instructions to all other components of the PCB.
Which is more important, the processor or the motherboard?
In comparing the processor vs. motherboard, we can find which one is more important. PCs cannot function without a processor. Since it sends instructions to the different components, it plays a vital role in the motherboard’s performance.
Additionally, the motherboard provides other functions like USB connectivity, wifi audio, Bluetooth, etc.
What is the relationship between the motherboard and the processor?
Quite simply, these two computers’ components are not the same because their functions, compatibility, and designs differ. This explains and organizes all the logical and arithmetic aspects of computer operation by the computer processor.
Like memory, processor, and other peripherals, the motherboard creates a new connection among the different components of the computer.
How long do motherboards maintain their processors?
When it comes to the computer, the processor is the most important component. Even though the motherboard supports just one socket, the central processing unit (CPU) initiates interactions with other components of the system.
Memory, storage, and various other devices are established in extension slots as well as inward and outward devices.
Are motherboards and processors the same thing?
The processor performs computations while the motherboard provides a platform for connecting the components of the computer.
Does the CPU function as the motherboard?
Computer cases contain components that perform specific roles inside. A mother board is a flat, large piece of silicon, and a central processing unit (cpu) is a network of chips installed on the motherboard.
How important is it to have a good motherboard or a good processor?
When compared to the motherboard, the processor is the most important part of the computer. Additionally, there is a processor socket on the motherboard that starts the communication between other important features and your central processing unit (CPU).
Conclusion
All of your confusion regarding Processor vs Motherboard will be resolved in our final decisions. It is not common knowledge that motherboards and processors perform various tasks. They perform an array of functions and assist the computer in maintaining its reliability.
There is one major difference between a processor vs motherboard that we consider, which is that a motherboard allows communication and creates contacts between various PC components such as processors, memory, and expansion slots and peripherals.
As a result, all the computer’s performance is intrinsically linked to the processor as it delivers its instruction and teachings to the various components to ensure that they perform authentically and reliably.
You may have to rebuild a new motherboard if your CPU is damaged out of date. There is no problem, since CPU sockets are established after a few years.
